Configuring an ASP.NET Core Web API Server
Creating the ASP.NET Core Web API
Step 1 - Create the New ASP.NET Core Web API Project
The steps below describe how to create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project. If you want to add the Analytics SDK to an existing application, go to Step 2.
1 - Start Visual Studio 2019 and click Create a new project on the start page, select the ASP.NET Core Web API template, and click Next.

2 - Provide a project name and set the location to the server directory we created eariler, and click Next.

3 - Choose your framework, authentication type, and Docker options, and then click Create.

Step 2 - Add Analytics SDK
1 - Right click the Solution, or Project, and select Manage NuGet Packages for Solution.
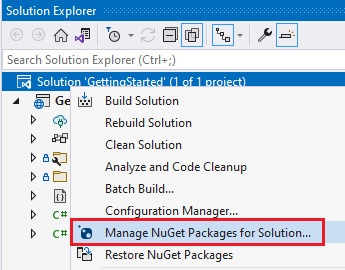
2 - In the package manager dialog, open the Browse tab, select the Infragistics (Local) package source, and install the Analytics.Sdk.Web.AspNetCore NuGet package into the project.
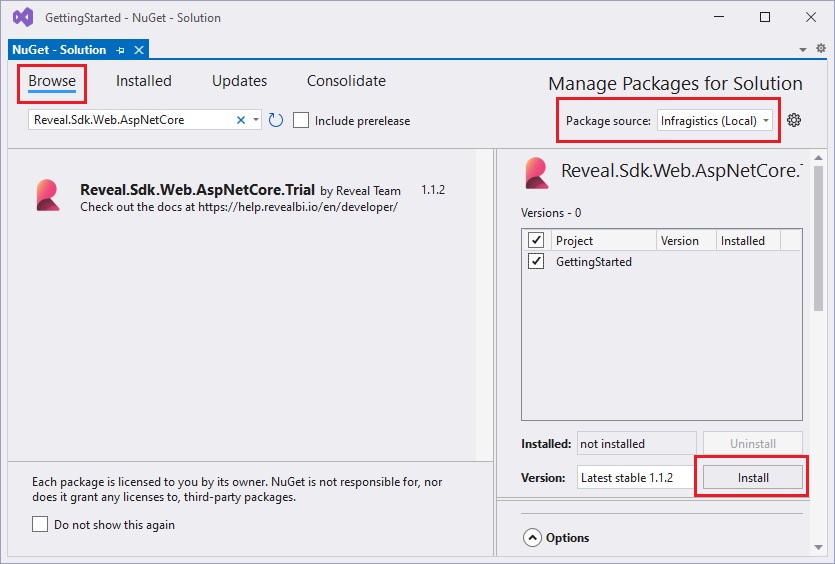
Note
If you are a trial user, you can install the Analytics.Sdk.Web.AspNetCore.Trial NuGet package found on NuGet.org.
3 - Open and modify the Program.cs file to add the namespace using Analytics.Sdk;. Then, add the call to IMcvBuilder.AddAnalytics() to the existing builder.Services.AddControllers() method as follows:
using Analytics.Sdk;
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddAnalytics();
Step 3 - Create the Dashboards Folder
1 - Right-click the project and select Add -> New Folder. The folder MUST be named Dashboards .
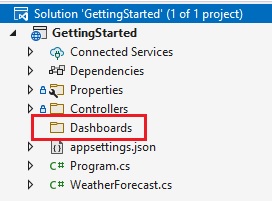
By default, the Analytics SDK uses a convention that will load all dashboards from the Dashboards folder. You can change this convention by creating a custom IRVDashboardProvider. You can learn more about this in the Loading Dashboards topic.
Step 4 - Setup CORs Policy (Debugging)
While developing and debugging your application, it is common to host the server and client app on different URLs. For example; your Server my be running on https://localhost:24519, while your Angular app may be running on https://localhost:4200. If you were to try and load a dashboard from the client application, it would fail because of ASP.NET Core's Cross-Origin Requests (CORs) security policy. To enable this scenario, you must create a CORs policy and enable it in the server project.
1 - Open and modify the Program.cs file to create a CORs policy which will allow any origin (url) access to any headers and methods.
builder.Services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("AllowAll",
builder => builder.AllowAnyOrigin().AllowAnyHeader().AllowAnyMethod()
);
});
2 - Apply the policy only while in debug mode. If you have a production application then you would apply the appropriate policy for your production builds.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseCors("AllowAll");
}
It's important to understand the order in which the middleware executes. The UseCors must be called in a specific order. In this example after UseHttpsRedirection() and before UseAuthorization(). For more information, please refer to this Microsoft help topic
Note
The source code to this sample can be found on GitHub.
Authentication Provider
TBD
Dashboard Provider
TBD
Data Provider
TBD
Data Source Provider
TBD
Export
TBD
Logging
TBD
AnalyticsEmbedSettings
CachePath
DataCachePath
LocalFileStoragePath
MaxDownloadSize
MaxInMemoryCells
MaxStorageCells
MaxStringCellSize
MaxTotalStringsSize
User Context Provider
TBD
